Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, has dominated headlines for over a decade. Since its inception in 2009, it has transitioned from an obscure digital experiment to a mainstream asset capturing the attention of investors worldwide. But given its notorious price volatility and the evolving regulatory landscape, many are asking: Is Bitcoin still a good investment? This article delves into the factors shaping Bitcoin’s investment potential and examines whether this digital asset deserves a place in modern portfolios.
Understanding Bitcoin’s Market Evolution
Bitcoin’s journey has been marked by phenomenal rises and sharp crashes. From trading at mere cents in its infancy to peaking above $68,000 in November 2021, Bitcoin has captured the imagination of investors seeking alternative assets. The underlying blockchain technology, decentralized nature, and capped supply of 21 million coins position Bitcoin as a “digital gold,” attracting individuals and institutional investors alike.
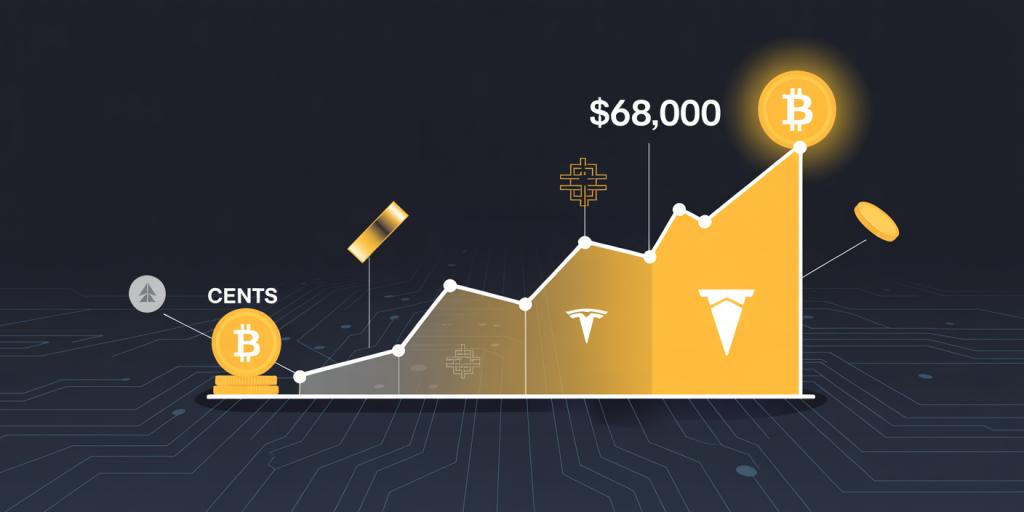
For instance, Tesla made headlines in early 2021 by purchasing $1.5 billion worth of Bitcoin, signaling growing corporate interest. Similarly, MicroStrategy, a business intelligence firm, has invested over $3 billion cumulatively in Bitcoin as a treasury reserve asset since 2020, illustrating how leading companies use Bitcoin to hedge against fiat currency depreciation. Yet, the asset’s inherent volatility and external risks remain significant considerations.
Statistical data show that Bitcoin experienced an average annualized return of approximately 230% from 2011 to 2021. However, the asset has also undergone multiple bubbles and corrections exceeding 80%, which can be unsettling for risk-averse investors. This complex dynamic underscores the importance of evaluating Bitcoin’s current investment potential within a broader economic context.
Bitcoin’s Volatility and Risk Profile Compared to Traditional Assets
Volatility is often cited as the primary risk of investing in Bitcoin. Daily price swings of 5-10% or more are not uncommon, even for established cryptocurrencies. When compared with traditional asset classes, Bitcoin’s risk-return profile is unique but challenging.
| Asset Class | Average Annual Return (2011-2021) | Annualized Volatility | Sharpe Ratio* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | 230% | 80% | 1.35 |
| S&P 500 (Equities) | 14% | 15% | 0.9 |
| Gold | 9% | 18% | 0.5 |
| US 10-Year Bonds | 4% | 7% | 0.6 |
*Sharpe Ratio measures risk-adjusted return
The table demonstrates Bitcoin’s extraordinary returns but highlights the significant volatility that accompanies these gains. Comparatively, traditional assets such as equities and bonds deliver steadier, albeit lower, returns. This disparity means Bitcoin may be suitable as a high-risk allocation within a diversified portfolio but less ideal for conservative investors seeking stability and predictable income.
Additionally, factors such as hacking incidents, regulatory developments, and market manipulation have periodically impacted Bitcoin’s price, intensifying risk exposure. For example, the Mt. Gox exchange hack in 2014 resulted in millions of dollars’ worth of Bitcoin being stolen, leading to a severe price crash and loss of investor confidence at the time. Risk management and due diligence remain critical when considering Bitcoin investment.
Institutional Adoption and Its Impact on Bitcoin’s Legitimacy
Institutional acceptance of Bitcoin has surged dramatically, significantly affecting its investment appeal. As regulations have become clearer and cryptocurrencies have gained legitimacy, financial institutions, hedge funds, and asset managers have started incorporating Bitcoin into their offerings.
Fidelity Digital Assets reports a steady increase in institutional Bitcoin investments, with over $5 billion in assets under custody by late 2023. The launch of Bitcoin futures ETFs, such as ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF in 2021, offered traditional investors regulated exposure to the asset without direct ownership, further fueling market participation.

Moreover, countries such as El Salvador have adopted Bitcoin as legal tender, an unprecedented move reflecting government-level acceptance, although its practical economic impact remains debated. Meanwhile, corporations using Bitcoin for payments and treasury management enhance its utility and visibility. For example, PayPal allows users to buy, hold, and sell Bitcoin on its platform, increasing accessibility.
Institutional involvement generally stabilizes markets by introducing professional trading strategies and reducing retail-driven speculation. However, it can also introduce new risks, such as centralized control over large Bitcoin holdings, which may influence price dynamics. Therefore, understanding institutional trends helps investors gauge Bitcoin’s evolving market maturity.
Regulatory Environment: Challenges and Opportunities
Regulation represents one of the most critical factors influencing Bitcoin’s viability as an investment. Governments worldwide are grappling with how to regulate cryptocurrencies, balancing innovation with consumer protection, anti-money laundering (AML), and tax compliance concerns.
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been cautious, rejecting several proposals for spot Bitcoin ETFs while approving futures-based alternatives. Meanwhile, countries like China have banned Bitcoin mining and trading, leading to a significant exodus of miners but not eradicating global Bitcoin activity.
On the positive side, regulation can legitimize markets, promote investor protection, and reduce fraudulent schemes. For instance, the European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation aims to create a harmonized crypto framework by 2024, providing clarity to investors and businesses.
However, excessive or unclear regulation may hinder adoption, increase transactional burdens, and depress prices due to uncertainty. In 2022, the U.S. experienced a crackdown on illicit cryptocurrency exchanges, which momentarily stirred market panic.
Investors must monitor regulatory developments as they can rapidly influence Bitcoin’s legality, accessibility, and taxation. A well-defined regulatory framework is likely to boost Bitcoin’s mainstream acceptance and foster sustainable growth.
Real-World Use Cases Enhancing Bitcoin’s Value Proposition
Bitcoin’s investment appeal extends beyond speculation; growing real-world applications contribute to its long-term value. As a decentralized digital currency impervious to censorship, Bitcoin offers unique advantages for cross-border payments, remittances, and store of value in economies with unstable currencies.
A real-life example is Venezuela, where hyperinflation has led to widespread adoption of Bitcoin as a hedge against currency collapse. Local merchants and individuals increasingly accept Bitcoin for goods and services, leveraging its inflation resistance and easy transferability via mobile wallets.
Similarly, the Lightning Network—a layer-2 scalability solution—has improved Bitcoin’s transaction speed and lowered fees, making microtransactions and daily payments more feasible. Companies like Bitrefill allow users to purchase gift cards and phone top-ups with Bitcoin, signaling growing utility.
Despite competition from newer cryptocurrencies offering faster and cheaper transactions, Bitcoin’s first-mover advantage and security continue to underpin its broader acceptance. For investors, these growing use cases suggest an expanding ecosystem supporting Bitcoin’s intrinsic value beyond mere price speculation.
Future Perspectives: What Lies Ahead for Bitcoin?
Looking forward, Bitcoin’s investment potential hinges on several emerging trends and macroeconomic factors. On one hand, continued inflationary pressures and concerns over fiat currency debasement may boost demand for Bitcoin as a digital store of value.
Recent data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) highlights an accelerating global debt load exceeding 350% of GDP, potentially straining governments’ fiscal capacity and fostering search for alternative assets. In such environments, Bitcoin’s capped supply and decentralized governance offer an appealing hedge.
Advancements in blockchain scalability, security, and regulatory clarity could also enhance Bitcoin’s user-friendliness and market penetration. Institutional investors may further increase allocations to digital assets as part of diversified portfolios seeking alpha generation.
However, risks remain significant. Geopolitical tensions, technological vulnerabilities, and the rise of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) could challenge Bitcoin’s dominance. For example, the introduction of CBDCs with quasi-cryptocurrency features might reduce the perceived need for decentralized alternatives.
It is thus prudent for investors to adopt a balanced approach, leveraging professional advice and periodic portfolio review. Bitcoin’s unique characteristics and evolving ecosystem suggest it remains a compelling, albeit volatile, investment option—particularly for those with high risk tolerance and a long-term horizon.
—
In summary, Bitcoin continues to represent an intriguing investment opportunity shaped by its transformative technology, expanding adoption, and evolving regulatory landscape. While volatility and risk factors are nontrivial, growing institutional interest and real-world use cases enhance its legitimacy. Investors considering Bitcoin should weigh its potential rewards against inherent risks and remain attentive to market developments.

Deixe um comentário